Table of Contents
- – Who Is The Best Civica Learning: Learning Mana...
- – Best Can Cpd Software Australia
- – What Is The Best Continuing Professional Deve...
- – What Are The Best Cubiko's Cpd Webinars Compa...
- – How Much Does The Cpd Management Tool - Upsk...
- – What Is The Best What Is Continuing Professi...
- – Whats The Best Completing And Tracking Your ...
What Is CPD for GPs in Australia? Continuing Expert Advancement (CPD) is a crucial element of practice for General Practitioners (GPs) in Australia, ensuring that they remain competent and capable of offering the highest requirement of care. As the health care landscape progresses, with new research, technologies, and treatment guidelines emerging, GPs must engage in continuous education and professional development. This blog checks out the significance of CPD for GPs in Australia, its requirements, and the various chances readily available for expert development.
Understanding CPD. CPD refers to the procedure of keeping, boosting, and documenting the understanding, abilities, and expert qualities that professionals require throughout their careers. For GPs, CPD involves a variety of academic activities created to enhance their medical practice, client care, and overall efficiency in their functions. CPD is not merely about fulfilling requirements; it is a commitment to lifelong learning and expert quality.
Why Is CPD Important for GPs? Staying Present: The field of medication is constantly progressing. New research findings, treatment methods, and scientific standards are routinely published, and GPs need to stay informed to provide the best possible care. Engaging in CPD enables GPs to keep abreast of these modifications and incorporate them into their practice.
Who Is The Best Civica Learning: Learning Management System Service? Australia
Regulatory Compliance: In Australia, GPs are required to fulfill specific CPD requirements set by the Medical Board of Australia and the Royal Australian College of General Practitioners (RACGP) Failure to fulfill these requirements can threaten their registration and ability to practice.
Enhancing Patient Care: CPD directly adds to enhanced client results. By taking part in relevant academic activities, GPs can enhance their clinical skills, expand their knowledge base, and use evidence-based practices, resulting in more efficient patient care.
Best Can Cpd Software Australia
Career Development: CPD supplies GPs with opportunities for profession improvement and specialization. By acquiring new skills and knowledge, GPs can check out various locations of practice, qualify for management functions, or even shift into other health care fields.
Building Professional Networks: Getting involved in CPD activities often involves engaging with peers and market experts. This networking fosters partnership, knowledge sharing, and assistance amongst specialists, improving the total learning experience.
What Is The Best Continuing Professional Development Australia
CPD Requirements for GPs in Australia. The Medical Board of Australia mandates that all registered medical specialists, including GPs, engage in CPD activities as part of their continuous expert development. The essential requirements for GPs include:

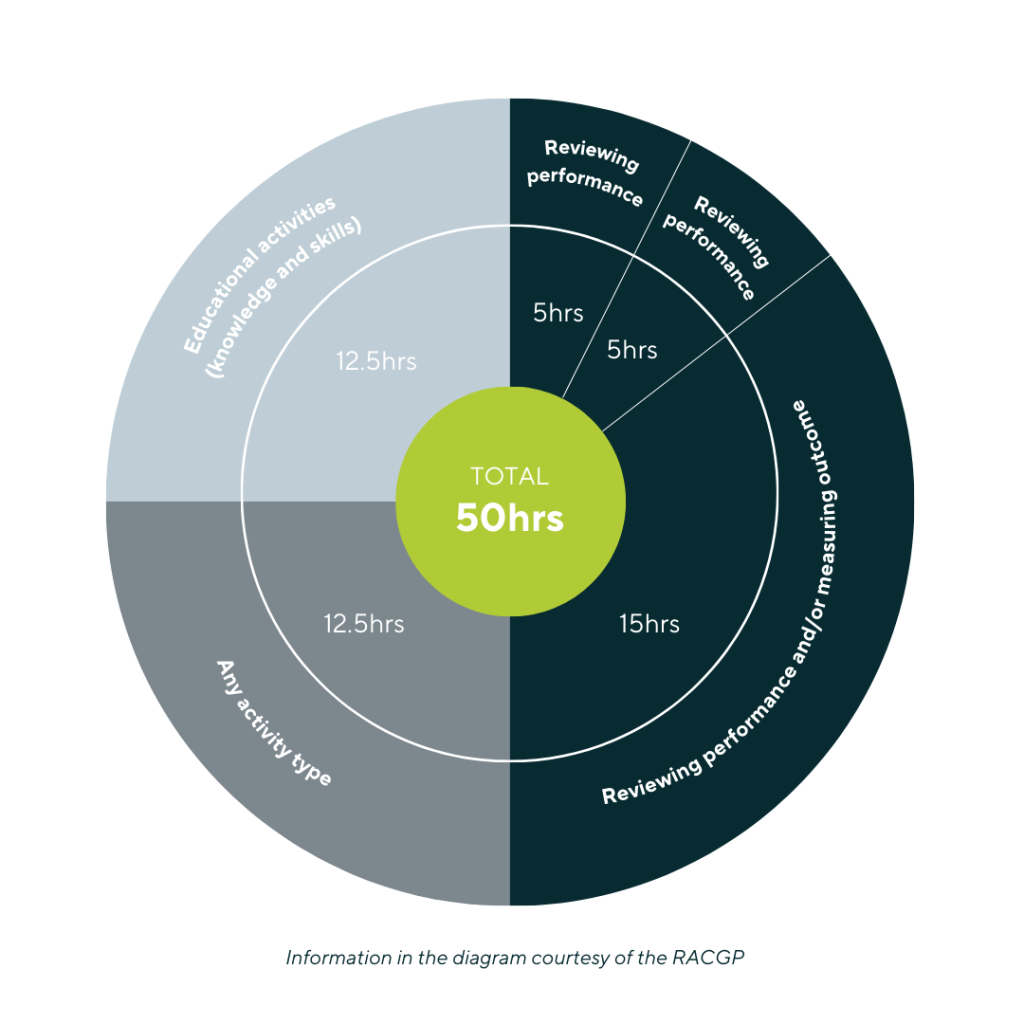
Minimum CPD Hours: GPs are required to finish a minimum of 50 hours of CPD each year. This includes a mix of instructional activities, with a minimum of 25 hours focusing on instructional activities pertinent to their practice.
What Are The Best Cubiko's Cpd Webinars Companies? Australia
Variety of Learning Activities: CPD activities can include a broad series of learning experiences, including workshops, conferences, online courses, self-directed knowing, and peer evaluations. GPs are motivated to participate in a range of activities to boost their learning experience.
Paperwork: GPs need to keep accurate records of their CPD activities, including the type of discovering carried out, the period, and how it relates to their practice. This documents is essential for demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements.
How Much Does The Cpd Management Tool - Upskill Service Cost? Australia
Opportunities for CPD for GPs in Australia - CPD for Health Professionals. Workshops and Conferences: Numerous expert companies, including the RACGP, host workshops and conferences customized for GPs. These occasions provide chances for hands-on learning, networking, and accessing the current research and clinical guidelines
Online Learning: With the development of digital platforms, GPs can access a variety of online courses and webinars. This flexibility permits them to find out at their own pace and fit CPD activities into their busy schedules.
Peer Review and Collaboration: Engaging in peer evaluation activities or working together with colleagues can be an important kind of CPD. Sharing experiences and discussing medical cases can result in much deeper insights and enhanced practice.
What Is The Best What Is Continuing Professional Development (Cpd)? In The World Right Now Australia
Self-Directed Learning: GPs can also participate in self-directed knowing through reading medical journals, looking into clinical guidelines, or taking part in appropriate online forums. This kind of finding out enables individualized education based on specific interests and requirements.
Whats The Best Completing And Tracking Your Cpd Australia
Specialized Training: GPs interested in advancing their abilities in specific locations, such as psychological health, chronic illness management, or emergency situation medication, can pursue specialized training programs or courses to deepen their knowledge.
Conclusion. Continuing Specialist Development is important for GPs in Australia, ensuring they remain qualified, notified, and efficient in offering premium client care. With particular CPD requirements set by regulative bodies, GPs must actively engage in different academic activities throughout their careers.
By welcoming CPD, GPs not just boost their understanding and skills but likewise contribute to enhanced client outcomes and the general improvement of the healthcare system. In a constantly altering medical landscape, a dedication to continuous knowing is not simply beneficial; it is a professional responsibility that ultimately boosts the quality of care offered to clients.
Table of Contents
- – Who Is The Best Civica Learning: Learning Mana...
- – Best Can Cpd Software Australia
- – What Is The Best Continuing Professional Deve...
- – What Are The Best Cubiko's Cpd Webinars Compa...
- – How Much Does The Cpd Management Tool - Upsk...
- – What Is The Best What Is Continuing Professi...
- – Whats The Best Completing And Tracking Your ...
Latest Posts
Orthodontics Jacksonville Dental Implants Quotes
Affordable Dental Implant Dentist Dental Implants In Jacksonville Florida Near Me
Best Local Affordable Dental Implant Quotes in Jacksonville, Florida
Navigation
Latest Posts
Orthodontics Jacksonville Dental Implants Quotes
Affordable Dental Implant Dentist Dental Implants In Jacksonville Florida Near Me
Best Local Affordable Dental Implant Quotes in Jacksonville, Florida